Author: SRI International
-
Human Engineering For Applied Natural Language Processing
Human engineering features for enhancing the usability of practical natural language systems are described. Such features include spelling correction, processing of incomplete (elliptical) inputs, interrogation of the underlying language definition through English queries, and an ability for casual users to extend the language accepted by the system through the use of synonyms and paraphrases.
-
Parametric Correspondence and Chamfer Matching: Two New Techniques for Image Matching
Parametric correspondence is a technique for matching images to a three dimensional symbolic reference map. An analytic camera model is used to predict the location and appearance of landmarks in the image.
-
Interactive Aids For Cartography and Photo Interpretation
In this report, the application areas of ARPA-supported Machine Vision work at SRI were changed to Cartography and Photointerpretation. This change entailed general familiarization with the new domains, exploration of their current practices and uses, and determination of outstanding problems.
-
LIFER: a Natural Language Interface Facility
This note describes LIFER, a practical facility for creating natural language interfaces to other computer software. Emphasizing human engineering, LIFER has bundled natural language specification and parsing technology into one convenient package.
-
Application Of Interactive Scene Analysis Techniques To Cartography
This paper proposes an interactive graphically generated method for delineation of cartographic and cultural features on a map.
-
Perceptual Strategies For Purposive Vision
This report describes a computer program that approaches perception as a problem-solving task. The system uses information about the appearances of objects, about their interrelationships, and about available sensors to produce a plan for locating specified objects in images of room scenes.
-
Experiments In Speech Understanding System Control
The main experiment tested the effects on performance of four major choices: focus attention by inhibition or use an unbiased best-first method, “island-drive’’ or process left or right, use context checks in priority setting or do not, and map words all at once or map only as called for.
-
Some Examples of AI Mechanisms for Goal Seeking, Planning, and Reasoning
In this paper we review some perhaps lesser know AI ideas that might also have utility in psychological modeling.
-
Msys: A System For Reasoning About Scenes
MSYS is a system for reasoning with uncertain information and inexact rules of inference. Its major application, to date, has been to the interpretation of visual features (such as regions) in scene analysis.
-
Subjective Bayesian Methods For Rule-Based Inference Systems
We describe in this paper a subjective Bayesian inference method that realizes some of the advantages of both formal and informal approaches. Of particular interest are the modifications needed to deal with the inconsistencies usually found in collections of subjective statements.
-
Knowledge Representation in Automatic Planning Systems
This paper is a tutorial on automatic planning systems with particular emphasis given to knowledge representation issues.
-
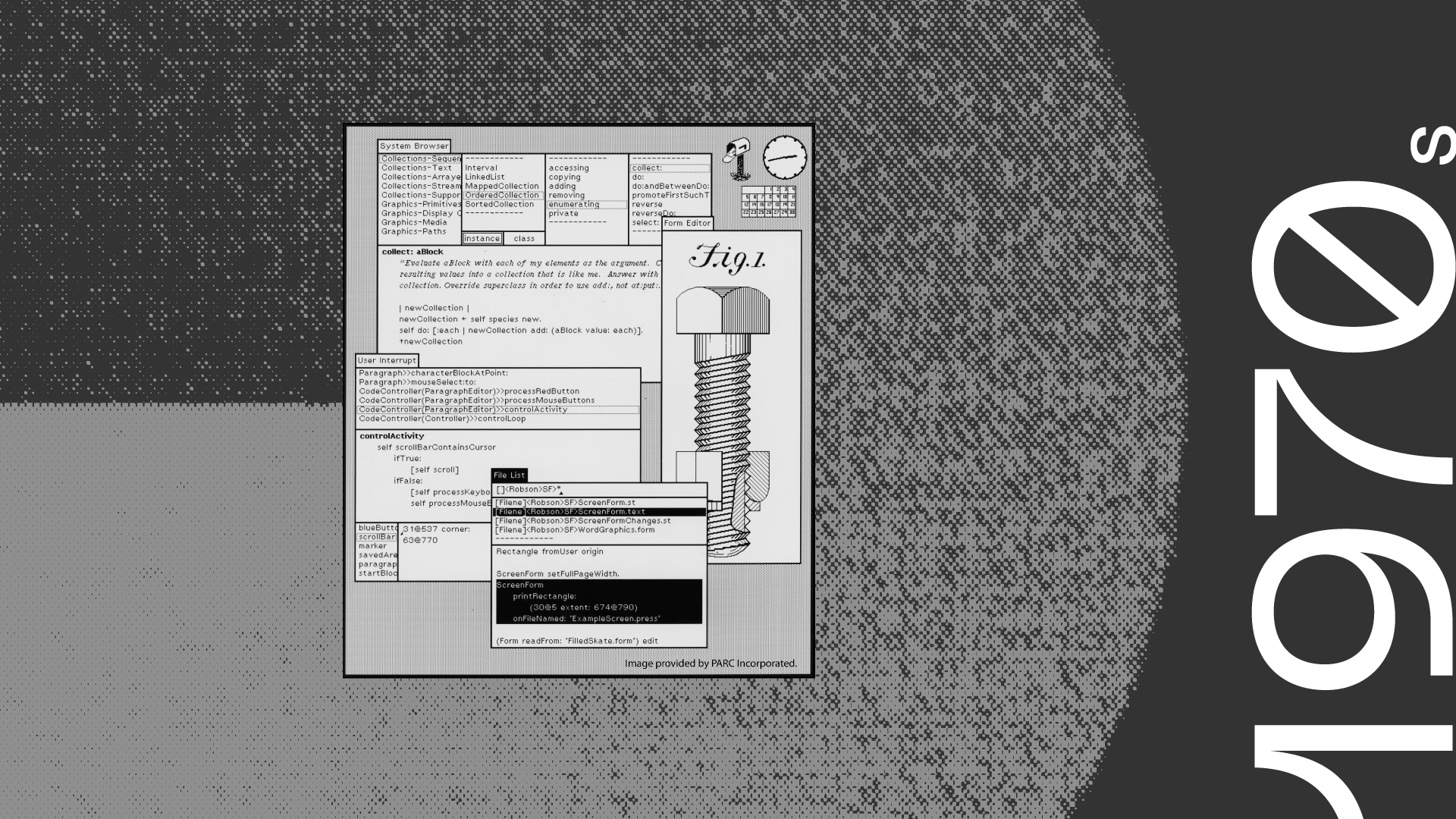
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
PARC, which is now part of SRI, debuted the first GUI, which used icons, pop-up menus, and overlapping windows that could be controlled easily using a point-and-click technique.