2D-3D reasoning and augmented reality
SRI has a strong portfolio of 2D-3D reasoning. This includes navigation and mapping using 2D and 3D sensors such as video and LIDAR.
In recent years, machine learning has significantly improved the semantic understanding of the 2D and 3D data. Incorporating semantics enables a new class of algorithms for navigation, Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), geo-registration, wide-area search, augmented reality, data compression, 3D modeling, and surveillance.
Semantic and GPS-denied navigation
CVT has developed highly efficient low-drift localization and mapping methods that exploit visual and inertial sensors. SRI has supported a large portfolio of programs and spin-offs using this technology. CVT has also incorporated high-level learning-based semantic information (recognition of objects and scene layouts) into dynamic maps and scene graphs, improving accuracy, efficiency, and robustness in our state-of-the-art navigation systems.
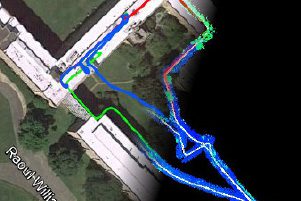
Long-range, wide-area, augmented reality
CVT has combined the localization and geo-registration methods described above with low-powered, compact, ruggedized hardware to create wide-area augmented reality applications. CVT has extended its augmented reality capabilities to work over multiple square kilometers while in GPS-challenged environments. This also includes long-range 3D occlusion-reasoning for augmented reality applications.

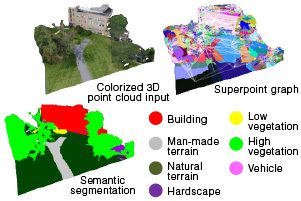
3D scene classification and modeling
CVT has developed extremely robust 3D scene classification methods over the last decade. These methods have now transitioned to Department of Defense (DoD) programs of record and commercially available software packages. Working with the Office of Naval Research (ONR), the U.S. Army and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA), CVT is now developing the next-generation 3D scene-understanding methods using machine learning. These methods incorporate top-down and bottom-up contextual reasoning and human-specified geographic rules within the learning process.
Surveillance
Recent publications
-
Machine Learning Aided GPS-Denied Navigation Using Uncertainty Estimation through Deep Neural Networks
We describe and demonstrate a novel approach for generating accurate and interpretable uncertainty estimation for outputs from a DNN in real time.
-
Vision based Navigation using Cross-View Geo-registration for Outdoor Augmented Reality and Navigation Applications
In this work, we present a new vision-based cross-view geo-localization solution matching camera images to a 2D satellite/ overhead reference image database. We present solutions for both coarse search for…
-
Cross-View Visual Geo-Localization for Outdoor Augmented Reality
We address the problem of geo-pose estimation by cross-view matching of query ground images to a geo-referenced aerial satellite image database. Recently, neural network-based methods have shown state-of-the-art performance in…
Featured publications
-
Long-Range Augmented Reality with Dynamic Occlusion Rendering
This paper addresses the problem of fast and accurate dynamic occlusion reasoning by real objects in the scene for large scale outdoor AR applications.
-
Striking the Right Balance: Recall Loss for Semantic Segmentation
We propose a hard-class mining loss by reshaping the vanilla cross entropy loss such that it weights the loss for each class dynamically based on instantaneous recall performance.
-
RGB2LIDAR: Towards Solving Large-Scale Cross-Modal Visual Localization
We study an important, yet largely unexplored problem of large-scale cross-modal visual localization by matching ground RGB images to a geo-referenced aerial LIDAR 3D point cloud.
-
Semantically-Aware Attentive Neural Embeddings for 2D Long-Term Visual Localization
We present an approach that combines appearance and semantic information for 2D image-based localization (2D-VL) across large perceptual changes and time lags.
-
Multi-Sensor Fusion for Motion Estimation in Visually-Degraded Environments
This paper analyzes the feasibility of utilizing multiple low-cost on-board sensors for ground robots or drones navigating in visually-degraded environments.
-
Augmented Reality Driving Using Semantic Geo-Registration
We propose a new approach that utilizes semantic information to register 2D monocular video frames to the world using 3D georeferenced data, for augmented reality driving applications.
-
Utilizing Semantic Visual Landmarks for Precise Vehicle Navigation
This paper presents a new approach for integrating semantic information for vision-based vehicle navigation.
-
Sub-Meter Vehicle Navigation Using Efficient Pre-Mapped Visual Landmarks
This paper presents a vehicle navigation system that is capable of achieving sub-meter GPS-denied navigation accuracy in large-scale urban environments, using pre-mapped visual landmarks.


